WHY THIS MATTERS IN BRIEF
We often think of materials as being static, but today “life” is being embedded into materials, and that opens the door to a whole new world of opportunities.
 Interested in the Exponential Future? Connect, download a free E-Book, watch a keynote, or browse my blog.
Interested in the Exponential Future? Connect, download a free E-Book, watch a keynote, or browse my blog.
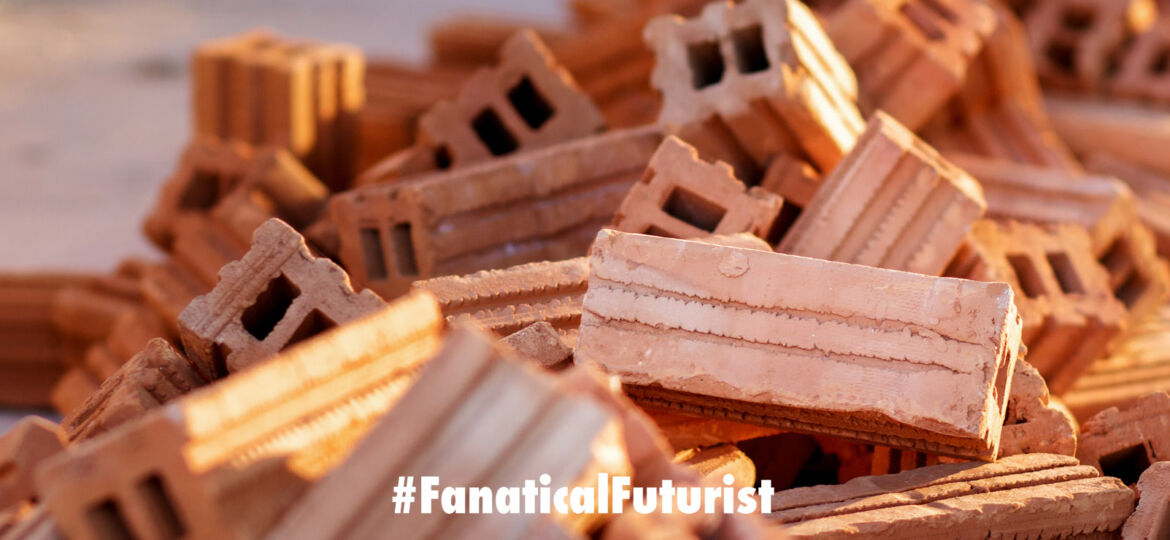
A simple combination of sand, gelatin and bacteria has been used for the first time to create “Living bricks” that can replicate themselves to make more bricks, and that are as strong as cement that could one day, it’s hoped, reduce the demand for said material that today accounts for 10 percent of all greenhouse gas emissions. Although that said recently I wrote about a new type of “green” concrete that also eliminates these emissions. And yes, you read the first sentence right these bricks can even reproduce – if a brick is cut in half then within a couple of days there are two more complete bricks. Now if we could only do that with money…
The technique capitalises on a process called Bio-Mineralisation, whereby living organisms produce minerals that can harden or stiffen tissue. The inspiration came in part from the limitations of self-healing concrete, itself a bio-mineralisation success story.
Here an inoculum of bio-mineralising bacteria is added to cement to heal cracks. However, the environment of cement is not conducive to biological growth.
“We showed that you can obtain greater survivability of the bacteria if you rethink the environment that you put them in,” explains Wil Srubar, part of the team at the University of Colorado Boulder that came up with the bricks.
In this system bacteria are placed in an environment that is more conducive to growth and through the bio-mineralisation process they contribute to the structural formation of the material. According to Srubar, “the compressive strength and mechanical properties we achieved are on the order of a cementitious mortar, like what you would see between the bricks in your house.”
The other advantage to increased survivability is that the bricks can be exponentially manufactured. Just like cell division, a parent brick can be divided to produce two new bricks. Srubar and his team were able to repeat the process for three generations in a single week, obtaining eight bricks from the original parent. The process involves heating the divided bricks until they are a medium viscosity liquid – sand solution, adding new gel medium and simply allowing the bacteria to grow for roughly six hours. From here more sand is added and the cubes cooled and re-molded to form new bricks.
The team’s challenge now is optimising the environment for the trade-off between the viability of the bacteria and structural capacity.
Kevin Paine, a structural engineer with the BRE Centre in Innovative Construction Materials at the University of Bath, says this is always a problem when working with bacterial systems.
‘The conditions that they need won’t stay ideal forever. They run out of food, oxygen or water and we need to give them that back. Furthermore, the best conditions for growth aren’t necessarily the best for structural integrity,” he said.
This was one reason that Srubar’s group chose to use cyanobacteria in their bricks as they are relatively resilient to stress. Cost wise they are also inexpensive and are photosynthetic too. Alongside scaling up the process the next steps are finding bacteria with desirable traits, such as desiccation resistance.
“This work is a platform for other researchers to infuse different biological functionalities into a structural material,” says Srubar. “Self-healing materials are the most common example but it could also be possible to create a material that senses and responds to airborne toxins or changes colour under certain kinds of light. Being a structural engineer myself I’m captivated by the ideas of building physical infrastructure out of a material like this.”
Paine agrees that the future of construction materials is living materials – although I’m not quite sure he’s ready to grow buildings quite yet out of this other new revolutionary living material that’s so life like it even metabolises. But maybe he will be one day…
“There’s a very exciting cooperation between biology and engineering which is only now starting to take off,” says Paine. “Engineers are starting to look at their materials problems in a different way and they are realising that biology has a lot of answers.”
Source: DOI 10.1016/j.matt.2019.11.016